Each year, the Latvian Academy of Sciences highlights the most outstanding work by researchers in both theoretical and practical science. This year, awards will be presented to 12 groups of scientists. Some of these studies have been ongoing and developing for years. One of last year's achievements in Latvian science is the creation of a unique device at the University of Latvia (UL) that will help determine how to improve the treatment for adenocarcinoma patients.
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma is one of the most aggressive types of cancer. Approximately 90% of patients diagnosed with it lose the battle with the disease within five years, as this tumor often does not respond to standard therapies.
This means that in order to fight this disease, individualized treatment approaches must be developed. Scientists at the University of Latvia (UL) are currently on the path to developing personalized therapy.
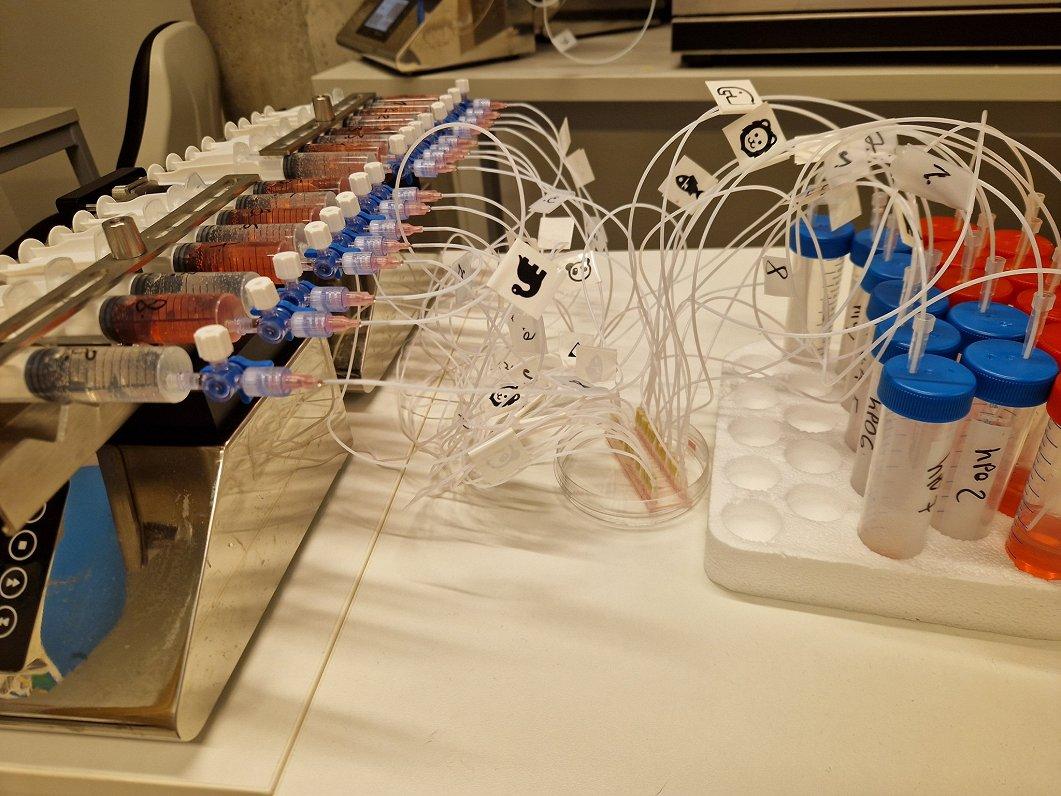
In collaboration with medical professionals, researchers obtain adenocarcinoma cells from operated patients, which they then propagate in the laboratory and try to understand which medications best eradicate the disease. To effectively deliver chemotherapy drugs to the tumor through blood vessel cells, scientists have created a unique microfluidic device in the National Research Program "Photonics," which mimics the interaction between the tumor and blood vessels. The device is the size of a matchbox, and in its center, researchers place microchips with tumor cells through which drugs travel via very fine channels.

The UL Professor of Medicine and leading researcher Una Riekstiņa explains: "In our small, miniature device, we can simulate a tumor, showing both the blood vessels and the tumor itself. What we can imitate is administering drugs through the flow, and then those drugs will be absorbed through the blood vessels in our small device, cross the vascular barrier, and reach the tumor cells. Then we can measure whether the tumor cells react to it. Essentially, effective drugs will be those that kill tumor cells. We can measure the signal that flows out of our device and indicates that the tumor cells do not like the drugs we provided."

Thus, just as in the human body, in the device, medications reach the tumor through blood vessels. Researchers also have the opportunity to observe whether the medication harms the blood vessels, allowing them to assess potential side effects. The study examines what happens to tumor cells over a longer period, for example, 50 days after therapy.
Another aspect revealed by the device is whether tumor cells detach and travel through the blood vessels. If this were to happen in a real human body, metastases would form.
The device can also signal if tumor cells do not respond to the medications and continue to grow.
Importantly, the device allows testing multiple medications on tumor cells simultaneously, which would not be possible in a patient's body, enabling researchers to compare results.
Additionally, the device can help identify new biomarkers that could be useful for tumor diagnostics in the future. The researcher explains that biomarkers are molecules secreted by the tumor, revealing its presence in the body.

Photo: Ilze Kuzmina
It should be noted that similar personalized therapies are being developed by scientists worldwide, aiming to adapt them for the treatment of various tumors.
When asked about the uniqueness of the device developed in Latvia, Riekstiņa responds: "The uniqueness lies in the fact that this device has a unique design created by our research group. We collaborate with the Institute of Solid State Physics, where these microfluidic chips are produced. These are small plates with embedded channels. These channels are matchstick-sized or even smaller, and we can connect them to tubes, add a pump, and circulate fluids. That’s microfluidics. It's called 'micro' because everything is at a very small scale, mimicking what happens in the human body."
The uniqueness also extends to how the blood flow imitation is constructed.
"This is a rapidly growing field, and it is anticipated that in 4–5 years, such a microfluidic organ-on-chip tool could assist doctors in deciding on the most effective therapy for a particular patient. This is also our goal. We are eager to develop this technology, but we need to build a statistical evidence base, test samples from multiple patients, and demonstrate that this method can reliably predict therapy sensitivity," Riekstiņa explains.
So far, researchers have analyzed the response of tumor cells from only three patients to medications administered using the device. Within the context of this study, scientists are not yet able to provide treatment recommendations to medical professionals. Before doing so, a broader evidence base is needed, and the new device must be certified as a medical device.
Additionally, efforts must focus on making the device more user-friendly. Riekstiņa states: "Only technology that is both easy to use and delivers reliable results will succeed. So, we are still in the development process."