Snowflakes are among nature's most exquisite works of art - each is unique, shaped under complex and ever-changing conditions. Why do snowflakes always have six arms? How do they develop such intricate yet symmetrical forms? From a scientific perspective, snowflake formation reveals how ice crystals emerge, develop patterns, and achieve their unparalleled uniqueness.
The essence of science is understanding what things are made of and how they work.
A snowflake is a single ice crystal in which water molecules are arranged in a precise hexagonal lattice.
Snow crystals form when water vapor in the air turns directly into ice, bypassing the liquid state. As more water vapor condenses onto the forming snow crystal, it grows larger and more elaborate, with intricate patterns emerging in the process. It is essential to note that snow crystals are not frozen raindrops; those are referred to as sleet.
Why such complex, symmetrical shapes?
The formation of a star-shaped snow crystal begins with a tiny hexagonal plate. As the crystal grows, arms extend outward. Falling through clouds, it encounters constantly changing temperatures and humidity levels, shaping each arm slightly differently at each stage.
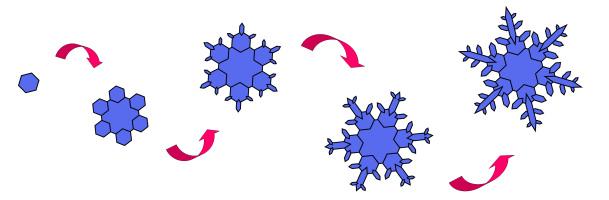
The exact shape of the crystal depends on its specific journey through the clouds. All six arms undergo identical changes simultaneously, leading to complex yet symmetrical patterns. Since no snow crystal follows the exact same path, no two snowflakes are completely identical. The six arms grow independently, yet under similar random conditions, they develop a comparable form, resulting in mostly symmetrical crystals.
Why six arms?
The six-arm symmetry of a snow crystal arises from the arrangement of water molecules in its hexagonal lattice. As this ice crystal model rotates, the hexagonal structure becomes apparent. The crystal has a three-dimensional form, and snowflakes are similarly three-dimensional. Star-shaped plates are thin and flat, while other shapes may vary. Snow crystals begin as hexagonal prisms, each with two bases and six prism faces.
There are also irregular snowflakes, as many snow crystals are not perfectly symmetrical. They grow rapidly, sometimes leading to random side branches. These combined processes occasionally result in both complex and symmetrical or asymmetrical crystals. Snowflake formation is intricate, and much remains unexplored.
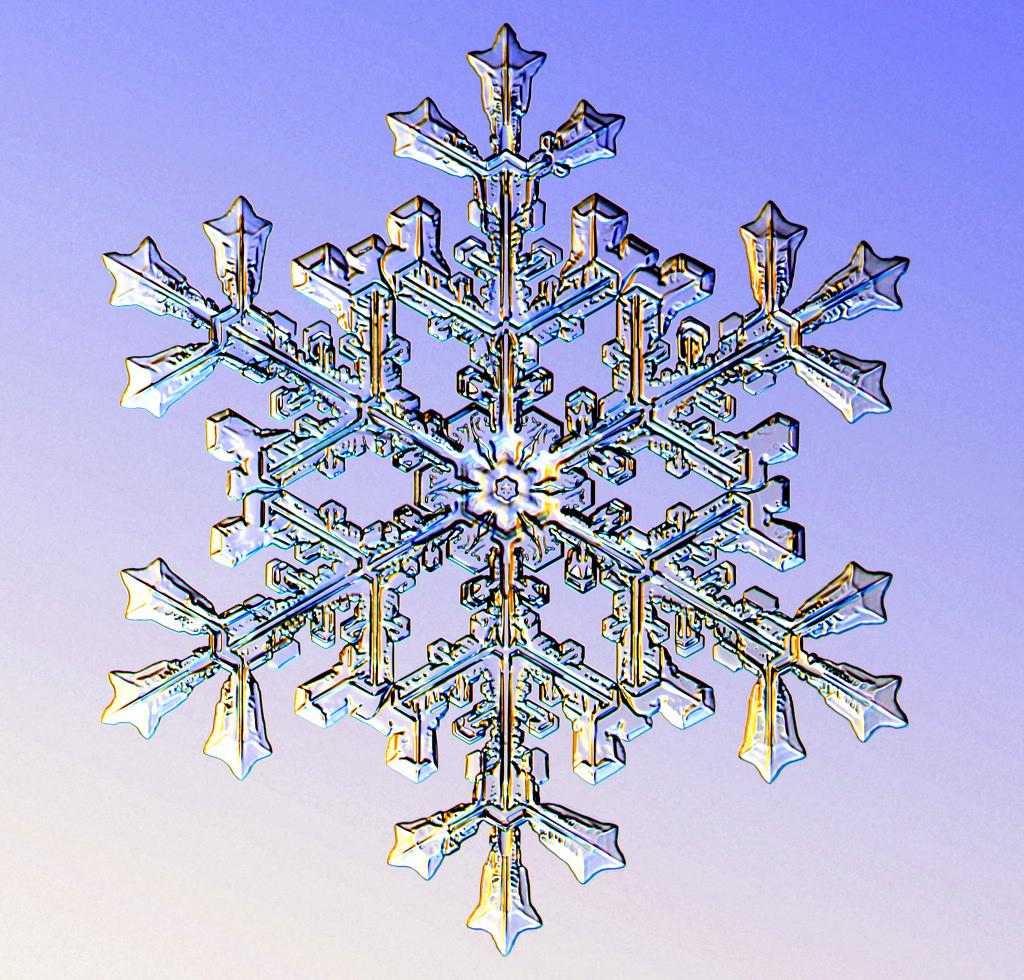

The symmetrical shapes and endless variety of snowflakes are closely tied to the microscopic processes within water molecules and their paths through clouds.
Each snowflake's formation is a unique result of the interplay of temperature, humidity, and atmospheric movements.
While science has explained many aspects of these processes, much about these crystalline works of art remains mysterious.


